- Turn on your computer so that Windows starts normally, insert the Windows 7 installation disc or USB flash drive, and then shut down your computer.
- Restart your computer.
- Press any key when prompted, and then follow the instructions that appear.
- On the "Install Windows" page, enter your language and other preferences, and then click Next.
- If the "Install Windows" page doesn't appear, and you're not asked to press any key, you might need to change some system settings. To learn how to do this, see Start your computer from a Windows 7 installation disc or USB flash drive.
- On the "Please read the license terms" page, if you accept the license terms, click I accept the license terms, and then click Next.
- On the "Which type of installation do you want?" page, click Custom.
- On the "Where do you want to install Windows?" page, click Drive options (advanced).
- Click the partition that you want to format and click Format.
COMPUTER EDUCATION 10
Tuesday, March 5, 2019
How to Reformat a Personal Computer
HOW TO REFORMAT A PERSONAL COMPUTER
Tuesday, February 19, 2019
What is a network address?
What is a network address
What is a Network Address?
A network address is also known as the numerical network part of an IP address. This is used to distinguish a network that has its own hosts and addresses. For example, in the IP address 192.168.1.0, the network address is192.168.1.
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/20969/network-address
Examples of Network IP Address
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/20969/network-address
Examples of Network IP Address
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) reserves the following IP address blocks for use as private IP addresses:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255.
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255.
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255.
Source:
IP Versions :
IPv4 - Internet Protocol Version 4
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet, and was the first version deployed for production in the ARPANET in 1983. It still routes most Internet traffic today,[1] despite the ongoing deployment of a successor protocol, IPv6. IPv4 is described inIETF publication RFC 791 (September 1981), replacing an earlier definition (RFC 760, January 1980).
source:
IPv6 - Internet Protocol Version 6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion. IPv6 is intended to replace IPv4.[1] IPv6 became a Draft Standard in December 1998, and became an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017.[2]
source:
HOW TO GET BINARY DIGIT/ HOW TO MAKE NETWORK ADDRESS?
*BINARY DIGIT HAS A TOTAL OF 255
Classes of IP Address :
| Class | Address range | Supports |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254 | Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks. |
| Class B | 128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254 | Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks. |
| Class C | 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254 | Supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks. |
| Class D | 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 | Reserved for multicast groups. |
| Class E | 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 | Reserved for future use, or research and development purposes. |
source:
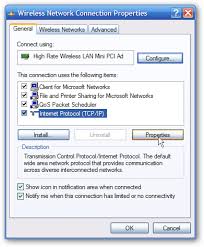
Steps on how to create an IP address:
- right click network places
- click properties
- right click local area connection
- click properties
- click TCP/IP
- click properties
- click OK
- right click network places
- click properties
- right click local area connection
- click properties
- click TCP/IP
- click properties
- click OK
- Steps on how to configure your IP Address:
-
- click start button
- click run
- type cmd
- type ipconfig
- type ping [IP address]
Wednesday, 3 October 2018
Wednesday, February 6, 2019
How to share file and printer in a computer network?
HOW TO SHARE FILE AND PRINTER IN A COMPUTER NETWORK?
Sharing file on Network (server)
- Replace the file inside the folder
- Right click the folder
- Click properties
- Click sharing
- Click share this folder on network
- Click apply
- and lastly click OK
Checking the file (client)
- Click start button
- Click run
- Then type \\ [IP address of the server]
Sharing printer on a Network (address)
- Click control panel
- Click add printer
- Right click printer
- Click sharing
- Click share this printer
- Click apply
- Click OK
Connecting printer on a Network (client)
- Click run
- Then type \\ [IP Address of server]
- Double click Printer and Faxes
- Right click printer
- Click connect
Wednesday, October 24, 2018
What are the different types of cable?
A.Twisted pair
A twisted pair cable is a type of cable made by putting two separate insulated wires together in a twisted pattern and running them parallel to each other. This type of cable is widely used in different kinds of data and voice infrastructures.
a.STP

Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable was originally designed by IBM for token ring networks that include two individual wires covered with a foil shielding, which prevents electromagnetic interference, thereby transporting data faster.
STP is similar to unshielded twisted pair (UTP); however, it contains an extra foil wrapping or copper braid jacket to help shield the cable signals from interference. STP cables are costlier when compared to UTP, but has the advantage of being capable of supporting higher transmission rates across longer distances.
 An optical fiber cable is a type of cable that has a number of optical fibers bundled together, which are normally covered in their individual protective plastic covers. Optical cables are used to transfer digital data signals in the form of light up to distances of hundreds of miles with higher throughput rates than those achievable via electrical communication cables. All optical fibers use a core of hair-like transparent silicon covered with less refractive indexed cladding to avoid light leakage to the surroundings. Due to the extreme sensitivity of the optical fiber, it is normally covered with a high-strength, lightweight protective material like Kevlar.
An optical fiber cable is a type of cable that has a number of optical fibers bundled together, which are normally covered in their individual protective plastic covers. Optical cables are used to transfer digital data signals in the form of light up to distances of hundreds of miles with higher throughput rates than those achievable via electrical communication cables. All optical fibers use a core of hair-like transparent silicon covered with less refractive indexed cladding to avoid light leakage to the surroundings. Due to the extreme sensitivity of the optical fiber, it is normally covered with a high-strength, lightweight protective material like Kevlar.
Optical fiber cable is widely used in fiber optic communications.
A twisted pair cable is a type of cable made by putting two separate insulated wires together in a twisted pattern and running them parallel to each other. This type of cable is widely used in different kinds of data and voice infrastructures.
a.STP

Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable was originally designed by IBM for token ring networks that include two individual wires covered with a foil shielding, which prevents electromagnetic interference, thereby transporting data faster.
STP is similar to unshielded twisted pair (UTP); however, it contains an extra foil wrapping or copper braid jacket to help shield the cable signals from interference. STP cables are costlier when compared to UTP, but has the advantage of being capable of supporting higher transmission rates across longer distances.
b.UTP
In an UTP cable, conductors which form a single circuit are twisted around each other in order to cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources. Unshielded means no additional shielding like meshes or aluminum foil, which add bulk, are used.
UTP cables are often groups of twisted pairs grouped together with color coded insulators, the number of which depends on the purpose.
B.Coaxial
A coaxial cable is a type of shielded and insulated copper cable that is used in computer networks and to deliver cable TV services to end users. It was first commercially implemented in the early 1940s and is used for both baseband and broadband data communication services.
Coaxial cable is also known as coax, which is derived from the geometric axis created between a shield and insulator.
C.Fiber optic
 An optical fiber cable is a type of cable that has a number of optical fibers bundled together, which are normally covered in their individual protective plastic covers. Optical cables are used to transfer digital data signals in the form of light up to distances of hundreds of miles with higher throughput rates than those achievable via electrical communication cables. All optical fibers use a core of hair-like transparent silicon covered with less refractive indexed cladding to avoid light leakage to the surroundings. Due to the extreme sensitivity of the optical fiber, it is normally covered with a high-strength, lightweight protective material like Kevlar.
An optical fiber cable is a type of cable that has a number of optical fibers bundled together, which are normally covered in their individual protective plastic covers. Optical cables are used to transfer digital data signals in the form of light up to distances of hundreds of miles with higher throughput rates than those achievable via electrical communication cables. All optical fibers use a core of hair-like transparent silicon covered with less refractive indexed cladding to avoid light leakage to the surroundings. Due to the extreme sensitivity of the optical fiber, it is normally covered with a high-strength, lightweight protective material like Kevlar. Optical fiber cable is widely used in fiber optic communications.
Difference Between Straight Through and Crossover Cable
Ethernet cables can be wired as straight through or crossover. The straight through is the most common type and is used to connect computers to hubs or switches. They are most likely what you will find when you go to your local computer store and buy a patch cable. Crossover cable is more commonly used to connect a computer to a computer and may be a little harder to find since they aren’t used nearly as much as straight through cable. Then, what’s the difference between them? Difference between straight through and crossover cables will be introduced in this blog.
T568A And T568B Wiring Standard Basis
A RJ45 connector is a modular 8 position, 8 pin connector used for terminating Cat5e or Cat6 twisted pair cable. A pinout is a specific arrangement of wires that dictate how the connector is terminated. There are two standards recognized by ANSI, TIA and EIA for wiring Ethernet cables. The first is the T568A wiring standard and the second is T568B. T568B has surpassed 568A and is seen as the default wiring scheme for twisted pair structured cabling. If you are unsure of which to use, choose 568B.
What Is Straight Through Cable?
A straight through cable is a type of twisted pair cable that is used in local area networks to connect a computer to a network hub such as a router. This type of cable is also sometimes called a patch cable and is an alternative to wireless connections where one or more computers access a router through a wireless signal. On a straight through cable, the wired pins match. Straight through cable use one wiring standard: both ends use T568A wiring standard or both ends use T568B wiring standard. The following figure shows a straight through cable of which both ends are wired as the T568B standard.
What Is Crossover Cable?
An Ethernet crossover cable is a type of Ethernet cable used to connect computing devices together directly. Unlike straight through cable, crossover cables use two different wiring standards: one end uses the T568A wiring standard, and the other end uses the T568B wiring standard. The internal wiring of Ethernet crossover cables reverses the transmit and receive signals. It is most often used to connect two devices of the same type: e.g. two computers (via network interface controller) or two switches to each other.
Choose a Straight Through or Crossover Cable?
Usually, straight through cables are primarily used for connecting unlike devices. And crossover cables are use for connecting unlike devices alike devices.
Use straight through cable for the following cabling:
Usually, straight through cables are primarily used for connecting unlike devices. And crossover cables are use for connecting unlike devices alike devices.
Use straight through cable for the following cabling:
- Switch to router
- Switch to PC or server
- Hub to PC or server
Use crossover cables for the following cabling:
- Switch to switch
- Switch to hub
- Hub to hub
- Router to router
- Router Ethernet port to PC NIC
- PC to PC
Conclusion
Straight through and crossover cables are wired differently from each other. One easy way to tell what you have is to look at the order of the colored wires inside the RJ45 connector. If the order of the wires is the same on both ends, then you have a straight through cable. If not, then it’s most likely a crossover cable or was wired wrong. At present, the straight through cable is much more popular than crossover cable and is widely used by people.
Straight through and crossover cables are wired differently from each other. One easy way to tell what you have is to look at the order of the colored wires inside the RJ45 connector. If the order of the wires is the same on both ends, then you have a straight through cable. If not, then it’s most likely a crossover cable or was wired wrong. At present, the straight through cable is much more popular than crossover cable and is widely used by people.
SOURCE:https://www.techopedia.com/definition/13433/twisted-pair-cable
http://www.cables-solutions.com/difference-between-straight-through-and-crossover-cable.html
http://www.cables-solutions.com/difference-between-straight-through-and-crossover-cable.html
Tuesday, October 23, 2018
What are the types of network topologies?
Star Topology
The most popular topology for business today - the star topology consists of all of the nodes on a network connected to a central switch or hub. A node is a device attached to the network - such as a computer.

Each node on the network has a cable back to the central switch. If one cable fails to a node, only that node (computer) is affected. You can combine several switches or hubs to create several stars, all connected together.
The Star topology is very inexpensive to maintain versus other topologies. 10BaseT is an example of Star topology. Think of the star topology as a big wheel. At the center of the wheel is a switch or hub and each spoke going out from the center goes to a node.
Bus Topology
Bus topology is one which all of the devices on the network are connected with a single cable with terminators on each end. This single cable is often referred to as a backbone or trunk.

The typical Bus network uses coax as its cable. Coax is a cable similar to what you use for your cable TV. Coax is also referred to as 10Base2.
The upside to using coax is that it is inexpensive, easy to install, and is not as susceptible to electromagnetic interference as twisted pair cable is.
The downside for a coax network is the speed is limited to 10 Mbps (Megabits per second) and that is an interruption occurs in the cable, all of the nodes (workstations) on the cable will lose connectivity. If a NIC fails or a cable is disconnected at any of the points in the network, it will not be terminated properly so all of the computers will lose connectivity to the network.
Mesh Topology
A mesh topology is one which all of the nodes are directly connected with all of the other nodes.

A mesh topology is the best choice when you require fault tolerance, however, it is very difficult to setup and maintain.
There are two types of mesh network: full mesh and partial mesh. A full mesh is one which every workstation is connected to the other ones in the network. In a partial mesh, the workstations have at least two NICs with connections to other nodes on the network. Mesh networks are commonly used in WANs.
Ring Topology
The ring topology is one which the network is a loop where data is passed from one workstation to another.

Commonly, you find the ring topology with token ring networks. Token ring networks are defined by IEEE 802.5 and were primarily developed by IBM. The token ring network is designed to transmit a token, or a special frame, designed to go from node to node around the ring. As the frame passes, if a workstation needs to transmit data, it modifies the frame, attaches its data and sends it on. If the data is intended for the next workstation on the network, it receives the data and the information stops at that workstation. If it is intended for somewhere else on the network, the data is retransmitted around the ring until it finds its intended location. Once the data finds its new home, a blank token is transmitted and another workstation can attach data and then that data travels around the ring.
There is a token holding timer to prevent a workstation from transmitting too much data. This protocol ensures all workstations on the network get an opportunity to send data. The original specification could only operate up to 16 Mbps though newer Fast Token Ring networks can transmit up to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second).
Advantages for token ring networks include a 4k maximum frame size, longer distance capabilities than Ethernet, and each station is guaranteed access to a token at some point. Ethernet is a shared access medium meaning each workstation has equal access to the available bandwidth at any given time.
The recommended distance for Type 1 cabling on a token ring network is 300 meters, on Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cabling, about 150 meters. More details will be discussed about token ring shortly\
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is an integration of two or more different topologies to form a resultant topologywhich has many advantages (as well as disadvantages) of all the constituent basictopologies rather than having characteristics of one specific topology.
.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
How to Reformat a Personal Computer
HOW TO REFORMAT A PERSONAL COMPUTER Turn on your computer so that Windows starts normally, insert the Windows 7 installa...